Research and Reports in Gastroenterology
All submissions of the EM system will be redirected to Online Manuscript Submission System. Authors are requested to submit articles directly to Online Manuscript Submission System of respective journal.
Track Your Manuscript
Explore SciTechnol
Google Scholar citation report
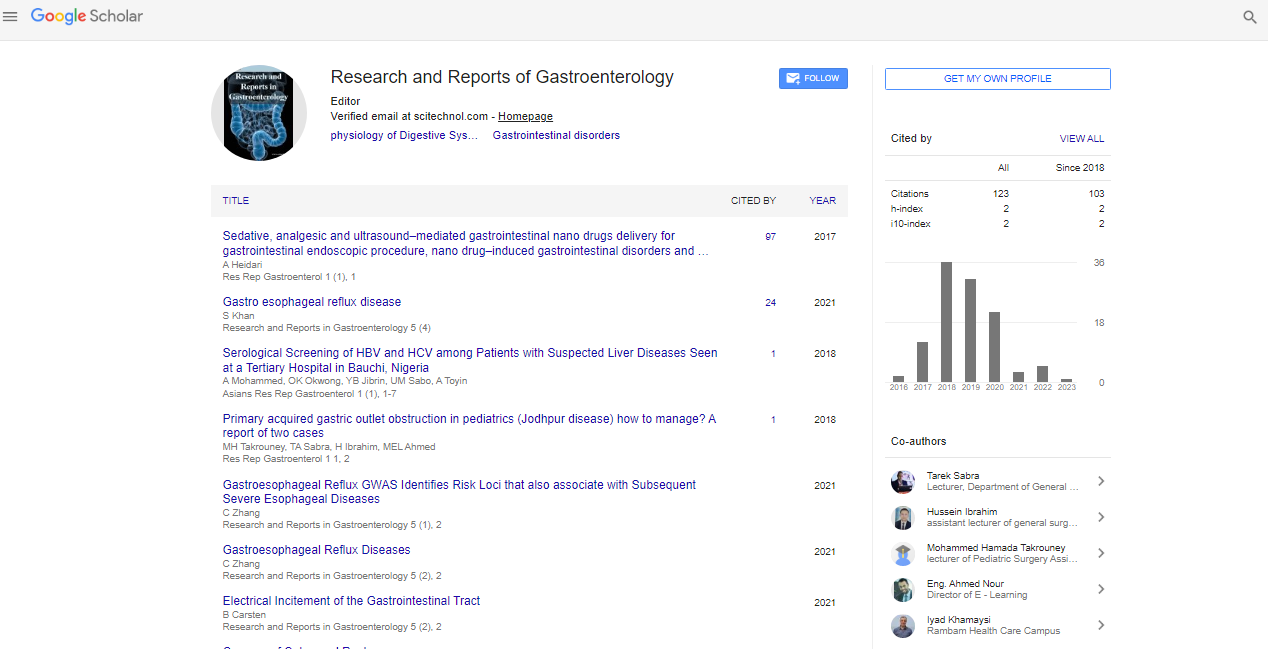
Citations : 121
Research and Reports in Gastroenterology received 121 citations as per Google Scholar report
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi