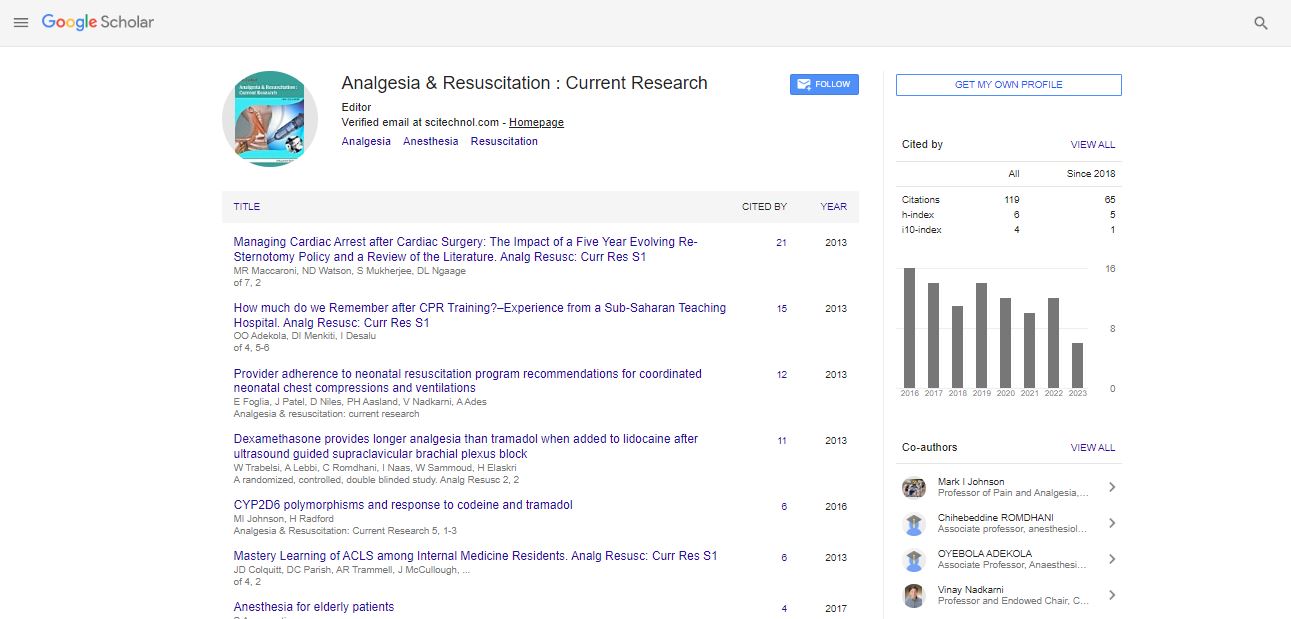
Short Communication, Analg Resusc Curr Res Vol: 12 Issue: 1
Antidepressant Medications and its Side Effects
Kevin Mark*
1Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences, University of South Florida, USA
*Corresponding Author: Kevin Mark
Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral
Neurosciences, University of South Florida, USA
E-mail: markcalmber@gmail.com
Received date: 01-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. ARCR-23-93260;
Editor assigned date: 03-Feb-2023, PreQC No. ARCR-23-93260 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 17-Feb-2023, QC No. ARCR-23-93260;
Revised date: 24-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. ARCR-23-93260 (R);
Published date: 03-Mar-2023, DOI: 10.4172/ 2324-903X.1000104.
Citation: Mark K (2023) Antidepressant Medications and its Side Effects. Analg Resusc: Curr Res 12:1.
Description
Antidepressant medications are commonly prescribed for the treatment of depression and other mental health disorders. These medications work by altering the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, which are responsible for regulating mood, appetite, and sleep. While antidepressants can be effective in treating these conditions, they also have potential side effects and risks that must be taken into consideration [1-4].
Types of antidepressant medications
There are several types of antidepressant medications, each with its mechanism of action and potential side effects [5]. The most commonly prescribed types include:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which helps regulate mood [6,7]. Examples of SSRIs include fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and citalopram (Celexa).
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): These medications work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, which helps regulate mood and energy levels [8]. Examples of SNRIs include venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta).
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): These medications work by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine, which helps regulate mood and energy levels [9]. Examples of TCAs include amitriptyline (Elavil) and nortriptyline (Pamelor).
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): These medications work by inhibiting the breakdown of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the brain, which helps regulate mood, energy levels, and appetite [10]. Examples of MAOIs include phenelzine (Nardil) and tranylcypromine (Parnate).
Antidepressant medications can have several potential side effects and risks that must be taken into consideration when prescribing these medications. Some of the most common side effects include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, Dry mouth, dizziness or light headedness, headache, insomnia or drowsiness.
Side effects
In addition to these side effects, there are also potential risks associated with antidepressant medications, including
Increased risk of suicide: While antidepressants can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression, they may also increase the risk of suicidal ideation, particularly in children and young adults.
Serotonin syndrome: This is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur when the levels of serotonin in the brain are too high, resulting in symptoms such as agitation, confusion, and rapid heartbeat.
Withdrawal symptoms: Discontinuing antidepressant medications can result in withdrawal symptoms, such as nausea, headache, and irritability [11].
Increased risk of bleeding: Some antidepressant medications, particularly SSRIs, can increase the risk of bleeding, particularly when taken with other medications or supplements that also increase the risk of bleeding.
Birth defects: Some antidepressant medications, particularly SSRIs, may increase the risk of birth defects when taken during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Antidepressant medications are an important tool in the treatment of depression and other mental health disorders. There are several types of antidepressants available, each with its mechanism of action and potential side effects. While these medications can be effective in reducing symptoms, they also have potential risks and side effects that must be taken into consideration when prescribing them. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment for their individual needs and to monitor for potential side effects and risks.
References
- Nakano M, Sourander A, Luntamo T, Chudal R, Skokauskas N, et al (2020) Early risk factors for postpartum depression: A longitudinal Japanese population-based study. J Affect Disord 269:148-153.
- Estiningtyas E, Cahyaningtyas AY, Sugiarsi S (2021) The effect of family support and social support on the incidence of postpartum depression. Jurnal Ilkes (Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan) 12(2):485-495.
- Chen Y, Ismail F, Xiong Z, Li M, Chen I, et al (2022) Association between perceived birth trauma and postpartum depression: A prospective cohort study in China. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 157(3):598-603.
- Baattaiah BA, Alharbi MD, Babteen NM, Al-Maqbool HM, Babgi FA, et al (2023) The relationship between fatigue, sleep quality, resilience, and the risk of postpartum depression: An emphasis on maternal mental health. BMC psychology 11(1):1-17.
- Corwin EJ, Brownstead J, Barton N, Heckard S, Morin K (2005) The impact of fatigue on the development of postpartum depression. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 34(5):577-586.
- Karl M, Schaber R, Kress V, Kopp M, Martini J, et al (2020) Precarious working conditions and psychosocial work stress act as a risk factor for symptoms of postpartum depression during maternity leave: Results from a longitudinal cohort study. BMC public health 20(1): 1-11.
- Botha E, Helminen M, Kaunonen M, Lubbe W, Joronen K, et al (2020) Mothers’ parenting self-efficacy, satisfaction and perceptions of their infants during the first days postpartum. Midwifery 88:102760.
- Selix NW, Goyal D (2015) Postpartum depression among working women: A call for practice and policy change. J Nurse Pract 11(9):897-902.
- Dagher RK, Govern PM, Alexander BH, Dowd BE, Ukestad LK, et al (2009) The psychosocial work environment and maternal postpartum depression. Int J Behav Med 16(4): 339-346.
- Chesak SS, Yngve KC, Taylor JM, Voth ER, Bhagra A, et al (2021) Challenges and solutions for physician mothers: A critical review of the literature. Mayo Clin Proc 96(6): 1578-1591.
- Kadale PG, Pandey AN, Raje SS (2018) Challenges of working mothers: Balancing motherhood and profession. Int J Community Med Public Health 5(7): 2905-2910.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi