Case Report, J Clin Exp Oncol Vol: 7 Issue: 1
Warty Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix with Lymph Node Metastasis: A Case Report with a Literature Review
Angel Danchev Yordanov1*, Stanislav Hristov Slavchev2, Strahil Asenov Strashilov3, Ivan Tzvetanov Malkodanski4, Borislava Ivova Dimitrova1, Ivan Nedkov Ivanov5 and Ilko Ivanov Iliev1
1Clinic of Gynecologic Oncology, University Hospital, Dr. Georgi Stranski, Pleven, Bulgaria
2Clinic of Gynecology, University Hospital “St. Anna”-Varna, Bulgaria
3Department of Plastic Restorative, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, Bulgaria
4Department of Critical care, Medical University, Pleven, Bulgaria
5Department of General and Clinical Pathology, University Hospital, Dr. Georgi Stranski, Pleven, Bulgaria
*Corresponding Author : Angel Danchev Yordanov
Clinic of Gynecologic Oncology, University Hospital, Dr. G. St ranski”-Pleven, Bulgaria
Tel: 00359 887671520
E-mail: angel.jordanov@gmail.com
Received: October 23, 2017 Accepted: January 02, 2018 Published: January 08, 2018
Citation: Yordanov AD, Slavchev SH, Strashilov SA, Malkodanski IT, Dimitrova BI, et al. (2018) Warty Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix with Lymph Node Metastasis: A Case Report with a Literature Review. J Clin Exp Oncol 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2324-9110.1000209
Abstract
Warty carcinoma of the cervix is a rare form of squamous cell carcinoma. This subtype has better prognosis than the highdifferentiated squamous cell carcinoma. It is known that it has lymph metastatic potential when vulva or penis are affected but as far as we know there are no described cases with lymph node metastases in literature for warty cervical cancer.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Warty carcinoma; Lymph node metastasis
Introduction
Warty carcinoma is a rare form of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the uterine cervix [1,2]. It has two components -condyloma and invasive squamous cell tumor. This histologic type has better prognosis, when compðred to well differentiated cervical sqðmous cell carcinoma. The most common locations of this tumor are in the anal and genital areas- vulva, vagina and uterine cervix, anus and penis. For most of the locations it occurs mainly in peri- and postmenopausal women, with the exception of vulvar warty carcinoma, which is most common in younger patients [3]. âhe involvement of the anus and the penis can be seen in young immunosuppressed men [3].
Although warty carcinoma is rarer than the other histologic types of cervical carcinoma, the latest research on this topic shows that it has better prognosis than the high-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma.
Case Report
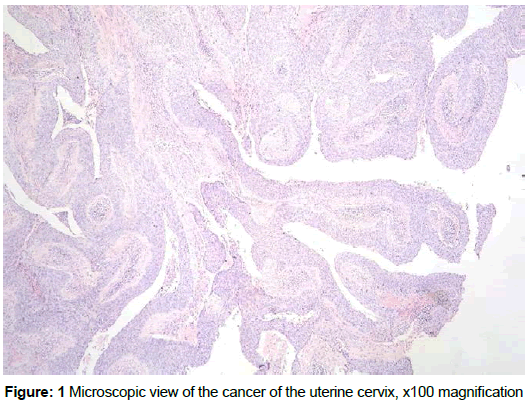
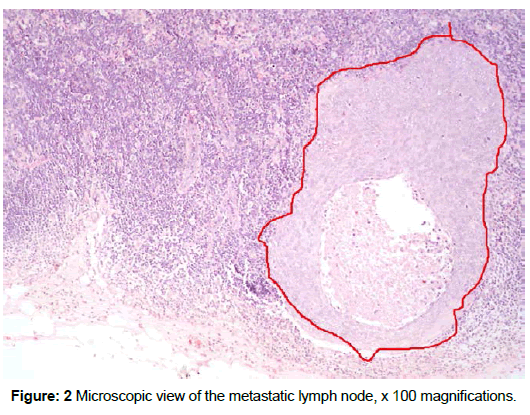
A multiparous 45-year-old woman was admitted to our clinic with history of postcoital bleeding for six months. She did not have medical history of other gynecological problems. The only surgical intervention she had was appendectomy. The general physical examination was without abnormalities. On pelvic examination the cervix was found to be hard, bulky and bleeding on touch. The parametrial ligaments were not involved. The other pelvic organs were without abnormalities. Rest of the systemic examination was normal, with normal blood count and normal ultrasound. Cervical biopsy was performed. The diagnosis SCC was made after histopathological examination of the surgical specimen. The patient underwent Class III radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection. Forty one lymph nodes were removed. Histological examination showed micrometastasis in two of them (Figure 1 and 2). The patient was staged according to FIGO TNM classification as pT1b2pN1M0. The patient’s postoperative period was uneventful. External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) therapy was performed 30 days after the intervention and remains free of disease for five years.
Discussion
Warty carcinoma of the uterine cervix is a rare variant of SCC. The tumor is frequently associated with HPV. As a clinical behavior, it stands between the verrucose and the low grade squamous cell carcinoma. It is usually described as a hybrid feature of invasive squamous cell carcinoma and the condylomata acuminate. Warty carcinoma has to be differentiated from condylomata acuminate and verrucous carcinoma by its feathery surface-stout and smooth keratotic surface. Verrucous carcinoma has characteristic bulbous rete pegs deep in the stroma and a complete absence of koilocytes [4]. Warty also differs from conventional squamous cell carcinomas by the presence of large numbers of atypical koilocytes [5]. It was thoroughly described as a malignant vulvar lesion and it is known that it has lymph metastatic potential when this area is affected [5]. The penile location of the same histologic type gives lymph metastases in 17-18%. As far as we know there are no described cases with lymph metastases in cases of warty cervical cancer in literature. There is one reported case of this type of cervical cancer with extension to the endometrial cavity [6] and one with left paraovarian metastasis, pouch of Douglas metastasis and right paratubal metastasis [3]. Importantly, in the present case, there were two lymph node micrometastasis out of the removed lymph nodes (total number of lymph nodes- 41). Up to this date (60 months) the patient is alive and well, and has no recurrence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, warty carcinoma is a rare type of cervical cancer. It has better prognosis than the SCC but the lymph node status should not be underestimated. Although there presence of lymph node involvement in this case, the patient is alive and free of disease. According to this finding, the lymph node metastasis may not affect the survival rate.
Conflict of Interest
The author has no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
References
- Wright TC, Ferenezy A, Kurman RJ (1994) Carcinoma and other tumours of the vulva. (4th Edition) Springer-Verlag, New York, USA: 298.
- Kurman RJ, Norris HJ, Wilkinson EJ (1992) Atlas of Tumour Pathologyy. Armed Forces Institute of pathology. Washington DC, USA: 75.
- Padberg BC, Bode B, Zimmermann D (2006) Metastatic Warty (Condylomatous) Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix Associated with Low-Risk HPV Type 6. Acta Cytol 50: 235-238.
- Cho NH, Joo HJ, Ahn HJ, Jung WH, Lee KG (1998) Detection of human papillomavirus in warty carcinoma of the uterine cervix: comparison of immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization and in situ polymerase chain reaction methods. Pathol Res Pract194: 713-720.
- de Silva MVC, Fernando MS , R Constantinem R, Hathotuwa R (2001) Warty (condylomatous) carcinoma of the cervix, a variant of invasive squamous cell carcinoma with less aggressive behavior. J Obstetrics Gyne 22: 31-32.
- Landeyro J, Gutiérrez-Fornés C, Sirvent JJ (2011) Warty (condylomatous) carcinoma of the cervix with extension to the endometrial cavity. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 112: 66-67.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi