Environmental radiology of Kelatan state, Malaysia
Nuraddeen Nasiru Garba, Ahmad Termizi Ramli and Muneer Aziz Saleh
Ahmadu Bello University, Nigeria
University Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
National Atomic Energy Commission, Yemen
: J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol
Abstract
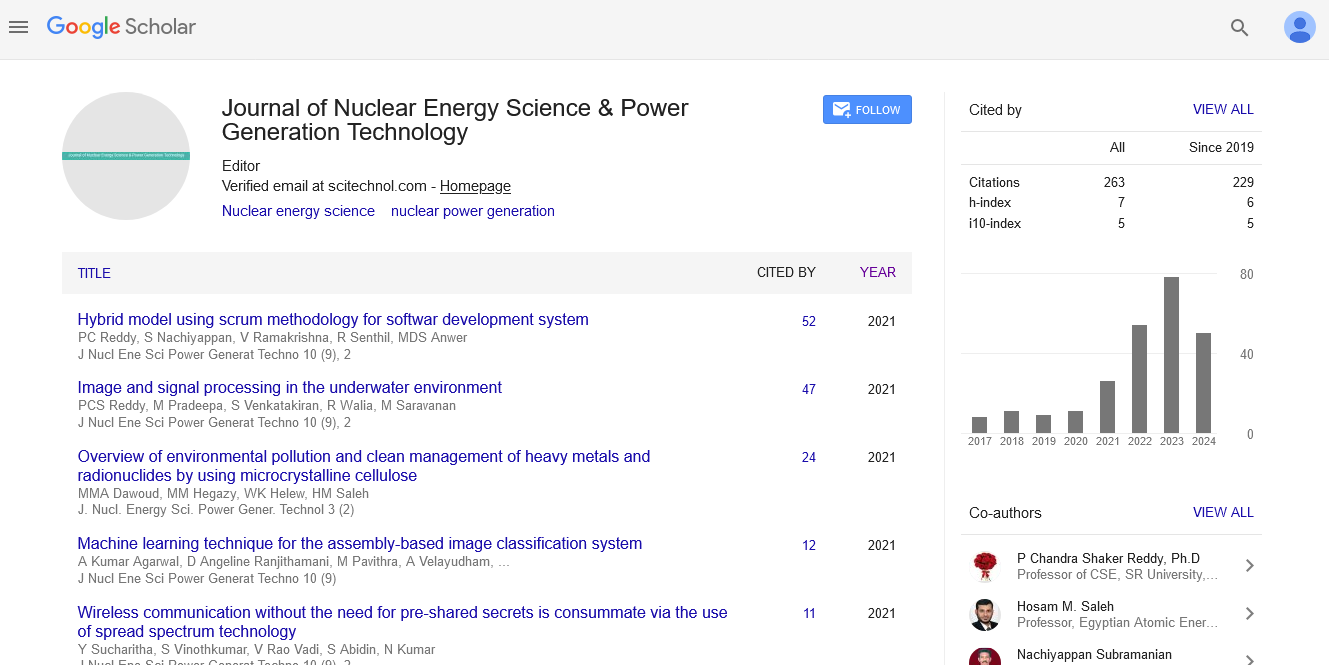
Natural environmental radioactivity arises mainly from primordial radionuclides such as 40K and also from 238U and 232Th decay series and has always been present in a variety of concentrations in every part of the earth’s mantle and in the tissue of every living being. Natural radioactivity can be found almost everywhere; in soil, public water supplies, oil and atmosphere. The present study was aimed of providing the base line data of Terrestrial Gamma Radiation Dose rates (TGRD), natural radioactivity concentrations and the corresponding radiological health hazards in the environments of Kelantan state, Malaysia. TGRD were measured using a micro roentgen survey meter model 19 manufactured by Ludlum, from 150 and 145 locations. A total of thirty six (36) soil and five (5) water samples from major rivers were collected. The soil samples were analyzed using a High Purity Germanium detector (HPGe) and Genie2000 software, while the water samples were analyzed at Malaysian Nuclear Agency using atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) for 40K and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) for U and Th activity concentrations. The measured TGRD mean values of 209 nGy h-1 which is about three times the world and two times Malaysian averages 59 nGy h-1 and 92 nGy h-1 respectively. The mean activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K in the soil samples were found to be 82 Bq kg-1, 123 Bq kg-1 and 643 Bq kg-1. 226Ra and 232Th are three times the world average values 32 Bq kg -1 and 45 Bq kg-1, while 40K is slightly higher than the world average value 420 Bq kg-1. For water samples, the mean activity concentrations of U and Th and activity concentration of 40K was found to be 13 mBq L-1, 4 mBq L-1 and 1119 mBq L-1. The health hazard impact of radium equivalent (Raeq), annual effective dose (AED), and external radiation hazard index (Hex) which are indicators of radiological health hazards were computed 307 Bq kg-1, 1.28 mSv y-1 and 0.83. Statistical relationships between TGRD with underlying geological formations and soil types were obtained. Isodose contour maps which shows the distribution pattern of TGRD for the state was produced. Radiological health due to TGRD and natural radioactivity are on the average higher than both the world average and Malaysian average but were still within the recommended values 370 Bq kg-1, 0.48 mSv y-1 and unity, thus should not pose any significant danger to the populations.
Biography
Nuraddeen Nasiru Garba holds a PhD degree in Physics (Radiological Health and Safety) from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia in 2016, MSc Radiation Biophysics from Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria in 2011 and BSc Physics from Bayero University, Kano in 2005. He is currently a Lecturer, Researcher and Postgraduate Programme Coordinator at the Department of Physics, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria-Nigeria. He was involved in teaching and research at both undergraduate and postgraduate levels and had published several scholarly articles in highly reputable peer reviewed journals. His area of interest includes environmental radiological assessment, radioecology, radiation protection and nuclear security.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi