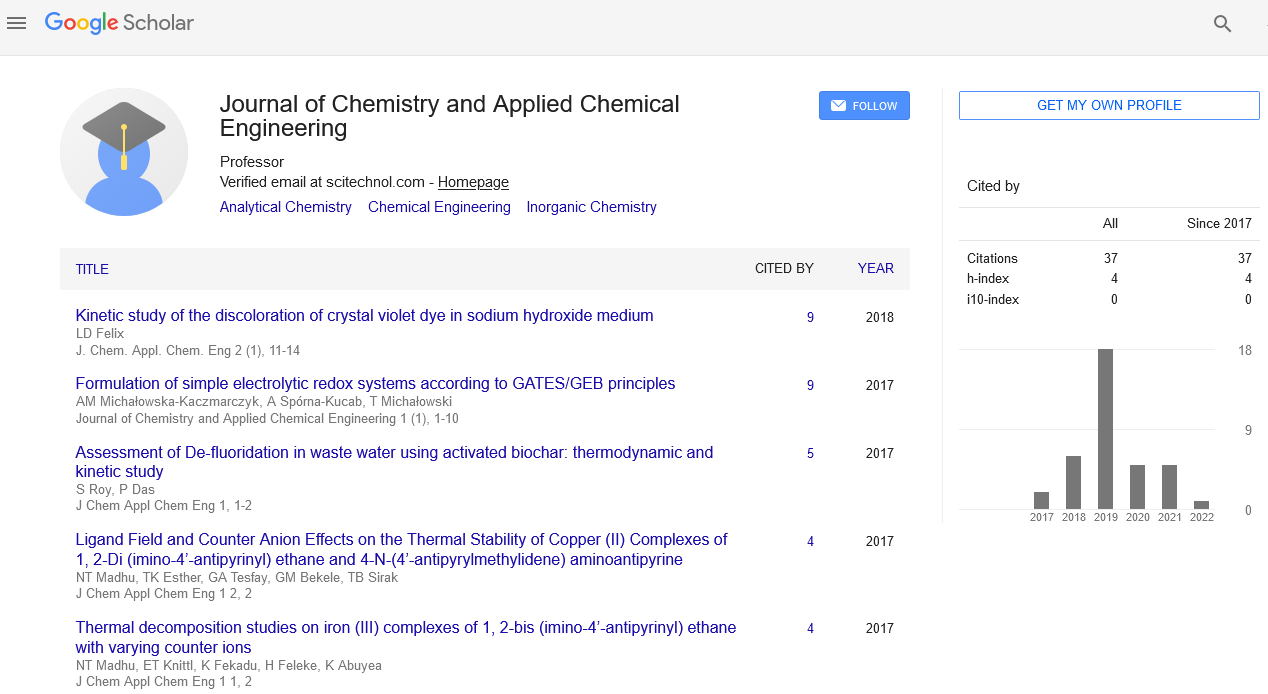
Synthesis, antibacterial activity of 3-amino 4,5,6-dimethoxyl-2-methyl derivatives via 4H-benzo[d] [1,3]-oxazine-4-one and quinazolin-4-(3H)-one
Osarumwense Peter Osarodion
Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Nigeria
: J Chem Appl Chem Eng
Abstract
Introduction: Compounds bearing a quinazoline moiety have been reported to possess a wide spectrum of biological and therapeutic properties, such as anti-inflammatory, antiplasmodial, antibacterial, antitumor, antimicrobial, antihelmintic and anticonvulsant properties. Objectives: This objective of this study was to eliminate the current challenges by synthesizing these novel antibacterial quinazolinone derivatives with a high anti-inflammatory potential. Methods: The condensation of 2-amino-methyl-4,5-dimethoxybenzoate with acetic anhydride yielded the cyclic compound 2-methyl-4,5-disubstituted-1,3-benzo-oxazine-4-one which further produce a novel 2,3-disubstituted quinazolin-4 ones via the reaction with hydrazine hydrate. The compounds synthesized were unequivocally confirmed by means of Infrared, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H and 13C), Gas chromatographymass spectrophotometer and elemental analysis. The synthesized compounds were screened and evaluated pharmacologically for their in-vivo anti-inflammatory activity and the paw volume of each rat was measured before 1 h and after 3 h of carrageenan treatment with the help of a plethysmometer. Results: Compound 1 had anti-inflammatory activity of 89.03% and 88.03% at 20 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg respectively, while compound 2 had anti-inflammatory activity of 94.79% and 90.30% at 20 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg respectively. Discussion: Compound 1 displayed a singlet signal at: δ3.78 attributed to methoxy group and singlet at δ3.68 which was due to methyl group. Other singlets appeared at δ7.16 and 6.40 attributed to aromatic protons. Also, 1H NMR spectrum of compound 2 showed a characteristic signal at δ2.56 (singlet) corresponding to methyl group and duplet at: δ3.90 for methoxy group. Two singlets appeared at δ7.41 and 7.10 attributed to aromatic protons. Another signal appeared at 5.80 which were attributed to the protons of the amino group. For the IR spectra, compound 1 was characterized by absence of υ NH2 and presence of υC-O stretch in 1101 cm-1 region of the compound. Compound 2 and 4 were characterized by absence of υC-0 and presence of υNH2 in 3301 cm-1 and 3300 region of the compounds. Compound 2 showed the highest anti-inflammatory activity at 20 mg.kg of 95.68% compared to compound 1 and indomethacin. These compounds synthesized had a higher antiinflammatory activity than indomethacin which is a standard anti-inflammatory drug. Conclusion: Compound 2 had a higher anti-inflammatory activity than Compound 1. The compounds synthesized had a higher anti-inflammatory activity than Indomethacin, a standard anti-inflammatory drug. Keywords: Anti-inflammatory activity, quinazoline-4(3H)-One, 5,6-dimethoxyl 2-methyl 4H–benzo[d] [1,3]– oxazine–4–One, nucleophile, synthesis, 3-amino-5,6-dimethoxyl-2-methyl quinazolin-4(3H)-One.
Biography
Osarumwense Peter Osarodion has completed his PhD at the age of 35 years from the University of Benin, Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. He is the Lecturer of Ondo State University of Science and Technology, Ondo State, Nigeria a premier University. He has published more than 30 papers in reputed journals and has been serving as an editorial board member of repute. He is interested in synthesis of novel Heterocyclic compounds and to determine their Antibacterial, Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory activity. He hopes to publish up to twelve (12) Journal papers and write a book during my full time postgraduate year.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi