Short Communication, J Fashion Technol Textile Eng S Vol: 0 Issue: 1
Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Conductive Knitted Fabrics
Merve Balkis1* and Huseyin Kadoglu2
1Institue of Fine Arts, Gazi University, Emek, Ankara, Turkey
2Textile Engineering Department, Engineering Faculty, Ege University, Turkey
Corresponding author : Merve Balkis
Institute of fine Arts, Gazi University, 06510, Emek /Ankara, Turkey
Tel: +90 312 216 22 81; Fax: + 90 312 215 15 99
E-mail: balkismerve@gmail.com
Received: May 21, 2015 Accepted: June 24, 2015 Published: June 27, 2015
Citation: Balkis M, Kadoglu H (2015) Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Conductive Knitted Fabrics. J Fashion Technol Textile Eng S1:008. doi:10.4172/2329-9568.S1-008
Abstract
Electromagnetic waves are known to have harmful effects on human health. The aim of this project is to investigate the application of knitted textile materials for the purpose of protection against electromagnetic waves and the effect of raw material, yarn and fabric parameters on electromagnetic shielding properties extensively. To obtain conductive textile surfaces, copper and silver filaments were used with cotton by using an apparatus on ring spinning machine.By using conductive yarns single jersey, rib,
and futter (2 threads) knitted fabrics were produced. Cotton fabrics were also produced for comparison.
Keywords: Electromagnetic waves; Electromagnetic shielding; Conductive knitted fabrics; Technical textiles
as copper, stainless steel, and aluminum. The above methods can be categorized under two headings, such as surface treatments and fillers. Surface treatments are often time consuming, labor intensive, and costly. Using fillers for shielding is more effective and cheaper than surfaces treatments [3].
Textile materials can be used for electromagnetic shielding applications when they are turned into electrical conductors. The most important factors effecting on the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of the textile surfaces are the amount of the conductive inclusion, conductivity property of the materials used, structure of the material surface and the conductive net [4].
The aim of this project is to investigate the application of knitted textile materials for the purpose of protection against electromagnetic waves and the effect of raw material, yarn and fabric parameters on electromagnetic shielding properties extensively.
Experimental
Copper and silver filaments were used to produce core yarns. For the feeding the metal filaments to the ring machine, a special apparatus were used. Three types of yarns were produced by using ring machine.
• The core yarns containing silver coated filaments with cotton sheath
• The core yarns containing fine copper filaments with cotton sheath.
• % 100 cotton yarns (for comparision)
By using core yarns three type knitted fabrics were produced; yarns single jersey, rib, and Futter (2 yarns). The copper filaments fineness are of 0,05 mm diameter.
2 yarn futter fabrics produced with 135 and 75 denier core filaments (Tables 1 and 2).
| Yarn Components | Fabric Structure | Fabric Name |
|---|---|---|
| 100% Ne 13 copper core yarn | Jersey | B1 |
| 66,7% Ne 13 copper core yarn, 33,3% Ne 22 cotton yarn |
Jersey | B2 |
| 50% Ne 13 copper core yarn, 50% Ne 22 cotton yarn |
Jersey | B3 |
| 33,3% Ne 13 copper core yarn 66,7% Ne 22 cotton yarn |
Jersey | B4 |
| 100% Ne 13 cotton yarn | Jersey | P |
Table 1: Names of the knitted fabrics containing copper filament.
| Yarn Structure | Core thickness | Yarn thickness | Fabric Structure | Fabric Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silver core yarn | 135 denier | Ne 27 | Jersey | GS1 |
| Silver core yarn | 135 denier | Ne 30 | Rib | GR1 |
| Silver core yarn | 135 denier | Ne 30 | Futter (2 thread) | GF1 |
| Silver core yarn | 75 denier | Ne 30 | Jersey | GS2 |
| Silver core yarn | 75 denier | Ne 30 | Rib | GR2 |
| Silver core yarn | 75 denier | Ne 30 | Futter (2 thread) | GF2 |
| Silver core yarn | 38 denier | Ne 30 | Jersey | GS3 |
| Silver core yarn | 38 denier | Ne 30 | Rib | GR3 |
| Silver core yarn | 38 denier | Ne 30 | Futter (2 thread) | GF3 |
| Cotton yarn | Ne 30 | Jersey | PS | |
| Cotton yarn | Ne 30 | Rib | PR | |
| Cotton Yarn | Ne 30 | Futter (2 iplik) | PF |
Table 2: Name of the knitted fabrics containing silver filament.
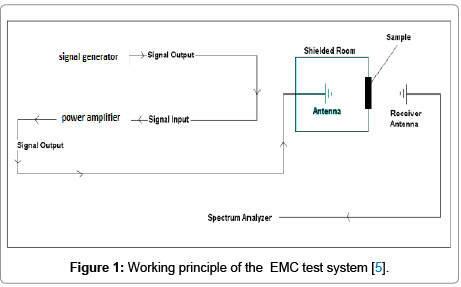
The shielding properties of the fabrics were tested by using EMC (Electromagnetic Competence) test system.
EMC test system is composed of a signal generator which produces the signals to be sent onto the sample, an RF power amplifier which amplifies the signals before being sent to the sample, two antennas; one is connected to the signal generator to send the signals to the sample and the other to the spectrum analyzer as receiver and a spectrum analyzer where the data is collected for evaluation. EMSE measurements were performed between 100 MHz-1 GHz frequencies according to EN50147-1 standard. The results were analyzed with SPSS statistics programme.
Results
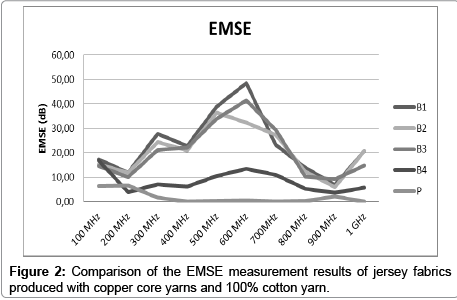
The results show that conductive fabrics have high EMSE (Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness) values when compared to cotton fabrics (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1: Working principle of the EMC test system [5].
Highest results were obtained with B1 which has the highest copper percentage in its structure. EMSE decreased with decreasing copper percentage in the structure.
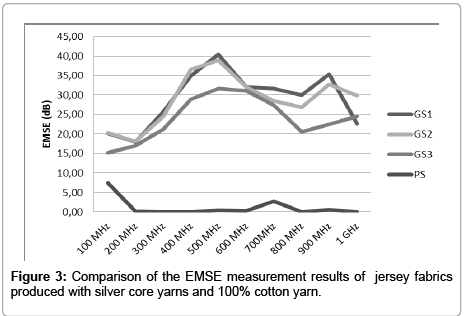
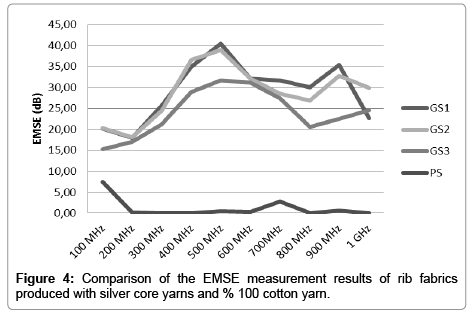
Figures 3-5 show that high EMSE (Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness) results can be obtained from the knitted fabrics produced with silver core yarns. It was observed that conductive fabrics have high EMSE values when compared to cotton fabrics. 2 yarn futter knitted fabrics showed higher values compared to jersey and rib fabrics, due to higher amount of conductive yarn in unit area of the fabric. It was also seen that higher shielding effectiveness results were obtained with conductive filaments in the structure. Therefore the highest results were obtained with GF1 and GF2 fabrics; which are compared to jersey and rib. Also the fabrics that contain copper have high EMSE values.
Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of the textile surfaces vary depending on type of material that is used. Also it is depending on the structure of textile surface.
Futter knitted fabrics show better values when compared to jersey and rib. Also the fabrics that contain copper have high EMSE values.
Discussion
Protecting human with textiles from electromagnetic interfence is possible. Type of the raw material, amount of the conductive filament in fabric structure and type of the knitted fabric structure have significant effects on electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. Copper and silver filaments have good conductivity. By using them as core, electromagnetic shielding can be provided.
Conclusions
In this study knitted fabrics were produced for the purpose of protection against electromagnetic waves.
The results show that conductive fabrics have high EMSE (Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness) values when compared to cotton fabrics. Futter knitted fabrics show better values when compared to jersey and rib. Also the fabrics that contain copper have high EMSE values.
Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of the textile surfaces vary depending on type of material that is used. Also it is depending on the structure of textile surface.
Increasing metal content in the fabric provides good EMSE (Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness) values according to SPSS results.
References
- Shie JW, Tien-Wei S (2013) The Reflection, Transmission and Absorbtion of Electromagnetic Waves in Stainless Steel/PolyesterFabrics.
- Das A, Kothari VK, Kothari A, Kumar A (2009) Effect of various parameters on electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of textile fabrics. IJFTR 34: 144-148.
- Cheng KB, Cheng TW, Nadaraj RN, Dev VRG, Neelakandan R (2006) Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of the Twill Copper Woven Fabrics. J Reinf Plast Comp 25: 699-709.
- Duran D, Kadoğlu H (2012) The Use of Electromagnetic Shielding Textiles in Medical Applications. International Congress on Healthcare and Medical Textiles, İzmir, Turkey.
- Duran D (2011) Tekstillerin Elektromanyetik Korumada Kullanilabilirliği Üzerine Bir Araştirma, Doktora Tezi, Tekstil Mühendisliği Anabilim Dali, Ege Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Turkey.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi