Heavy metal-induced up regulation of anti-oxidative enzymes and hemolymph biochemical compositions in Oxya hyla hyla (Serville)
Iqra Azam, Sumera Afsheen and Muhammad Kaleem Sarwar
University of Gujarat, Pakistan
: Forensic Toxicol Pharmacol 2015, 4:3
Abstract
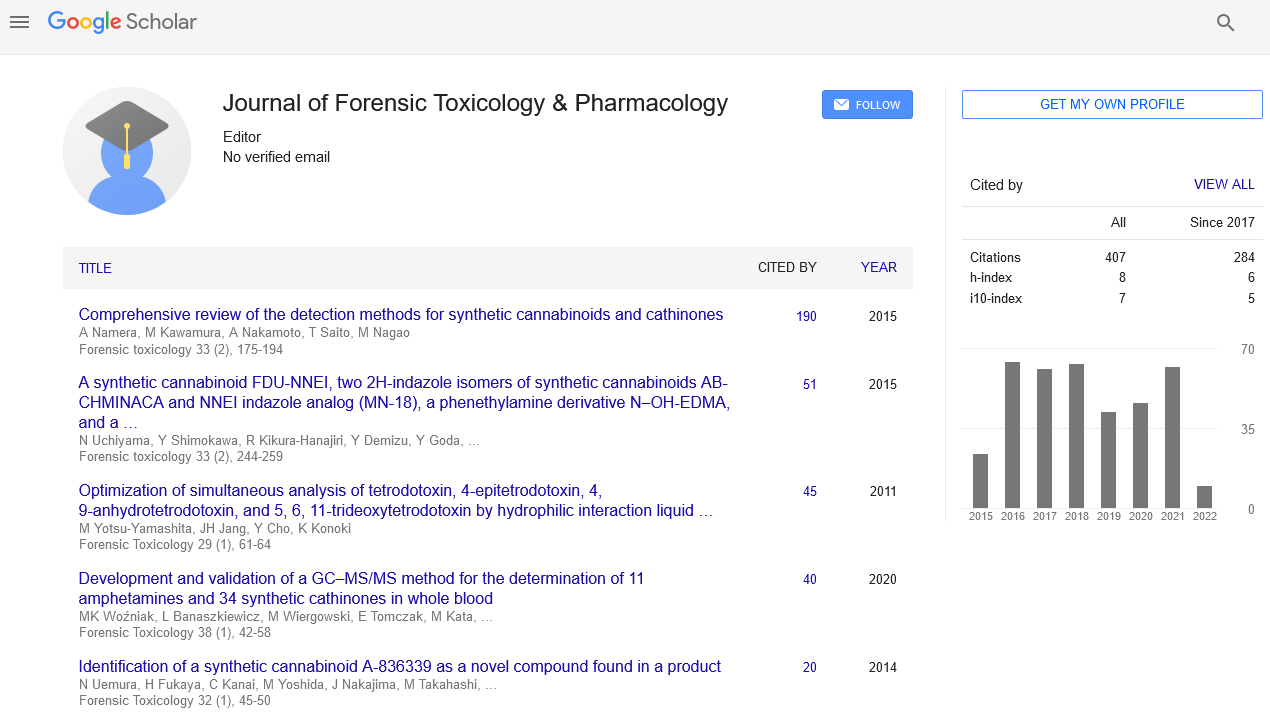
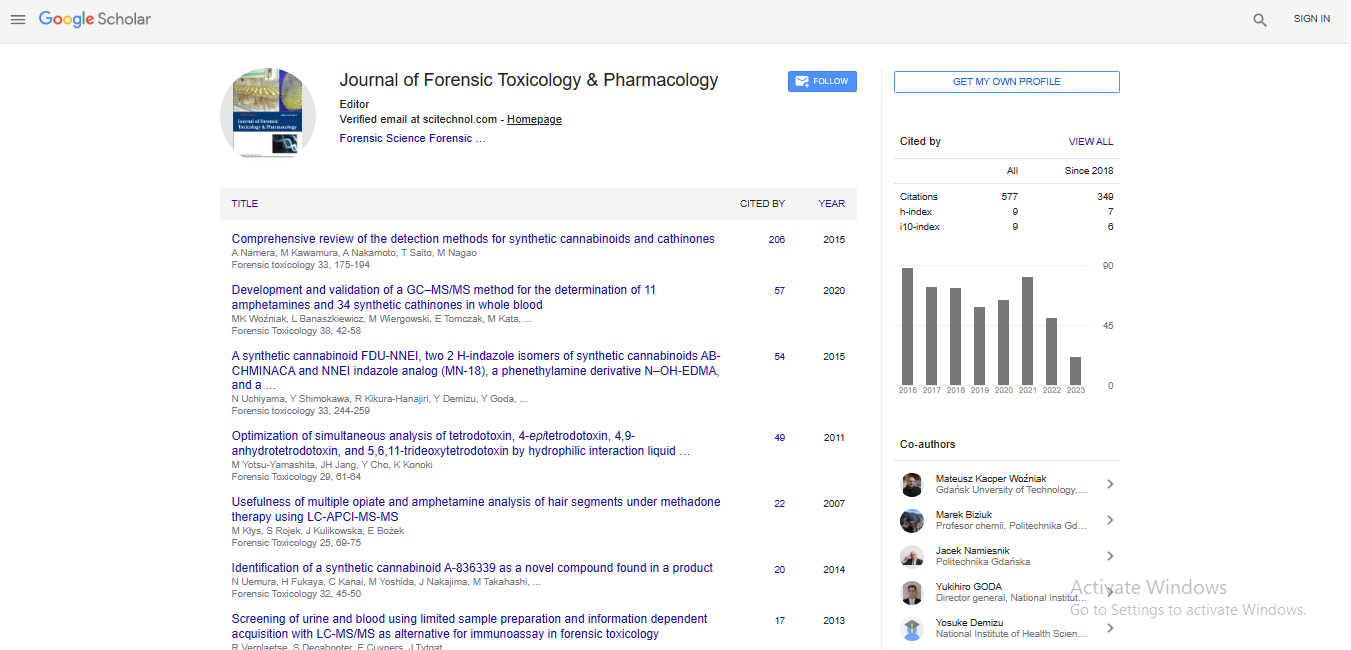
Present study was conducted to determine toxic effects of heavy metals (Cd, Pb and Hg) on antioxidant enzymes of a grasshopper species i.e., Oxya hyla hyla (Serville). Changes in the activities of antioxidant enzymes [superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), lipid peroxidation (LPO)] and biochemical composition of hemolymph were measured by exposing trailed insect to Cd+2, Pb+2 and Hg+2 at different concentrations (0, 0.50×10-4, 1.10×10-4, 1.55×10-4gg-1) of CdCl2, PbCl2 and HgCl2 for variable exposure time (24, 50 and 75 hours). The insect showed significant accumulation of metals with the increase inexposure of dose and time. The SOD activity was lowered at 1.10×10-4 to 1.55×10-4gg-1 than at 0.50×10-4gg-1 Cd+2, Pb+2 and Hg+2 levels. Detoxification effect was expressed by SOD at low metal concentrations and this effect disappeared at high concentrations. Assayed activities of CAT, POD and LPO level were significantly accelerated and correlated positively as metal exposure time increased showing species dependency. A significant decrease in total soluble protein, sugar, lipids and glycogen contents was observed due to metal exposure throughout the entire tested period except after the first 24 hours of exposure at the lower concentrations. Thus CAT had a strong detoxification effect as compared to SOD whereas POD had a weak detoxification effect. The study thus concludes that O. hyla hyla (Orthoptera: Acrididdae) and its antioxidant enzyme level can be used as bioindicator and bio marker of biotic and abiotic stresses.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi