Research Article, J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng Vol: 3 Issue: 1
Applying Wavelet Decomposition Hydrological Time Series and the Optimization of Model Groups in Flood Forecasting
| Chien-Ming Chou* |
| Department of Design for Sustainable Environment, MingDao University, 369 Wen-Hua Road, Peetow, Changhua 52345, Taiwan |
| Corresponding author : Dr. Chien-Ming Chou Department of Design for Sustainable Environment, MingDao University, 369 Wen-Hua Road, Peetow, Changhua 52345, Taiwan Tel: +886-4-8876660 E-mail: jamin@mdu.edu.tw |
| Received: November 14, 2013 Accepted: January 15, 2014 Published: January 20, 2014 |
| Citation: Chou CM (2014) Applying Wavelet Decomposition Hydrological Time Series and the Optimization of Model Groups in Flood Forecasting. J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng 3:1. doi:10.4172/2325-9647.1000111 |
Abstract
Applying Wavelet Decomposition Hydrological Time Series and the Optimization of Model Groups
in Flood Forecasting
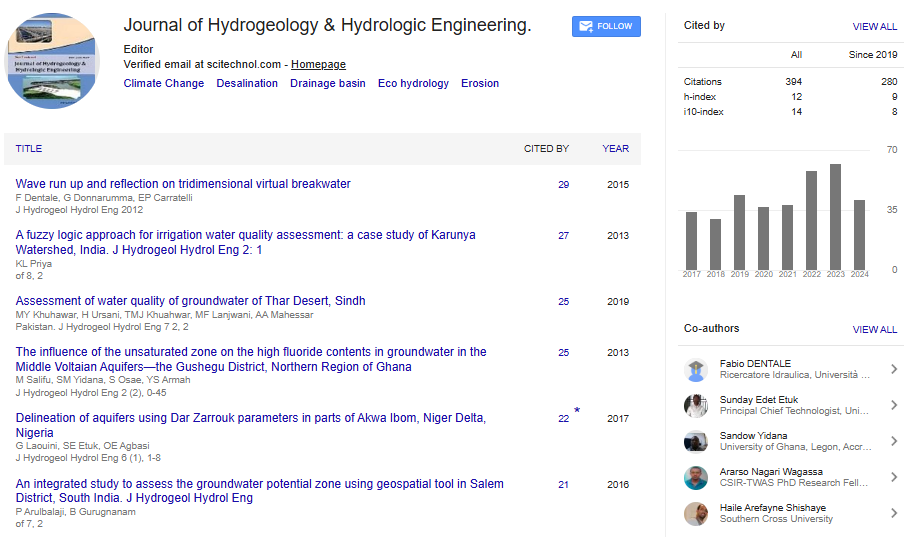
This study applies a redundant wavelet transform (WT) and an optimization of model groups to accurately forecast the flood of a watershed. Effective rainfall and direct runoff can be decomposed into detailed signals and an approximation by using a redundant WT. The AutoRegressive model with exogenous Input (ARX), nonlinear ARX (NARX), time-varying ARX, and time-varying NARX models are implemented in parallel at each resolution level, and the optimal model is selected as the forecasting model. The summation of the forecasting results obtained at various resolution levels yields the overall flood forecasting by applying the inverse WT. The first-stage validation results indicate that the optimalforecasting model at each resolution level for six events is timevarying NARX. The second-stage validation results show that the proposed approach is appropriate for modeling the rainfall-runoff process at each resolution level and estimating the overall runoff for small watersheds in Taiwan. The analytic results also confirm that the proposed wavelet-based method outperforms the conventional method, which uses data only at the original resolution level, because of the multi-resolution analysis (MRA) property of the wavelet transform.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi