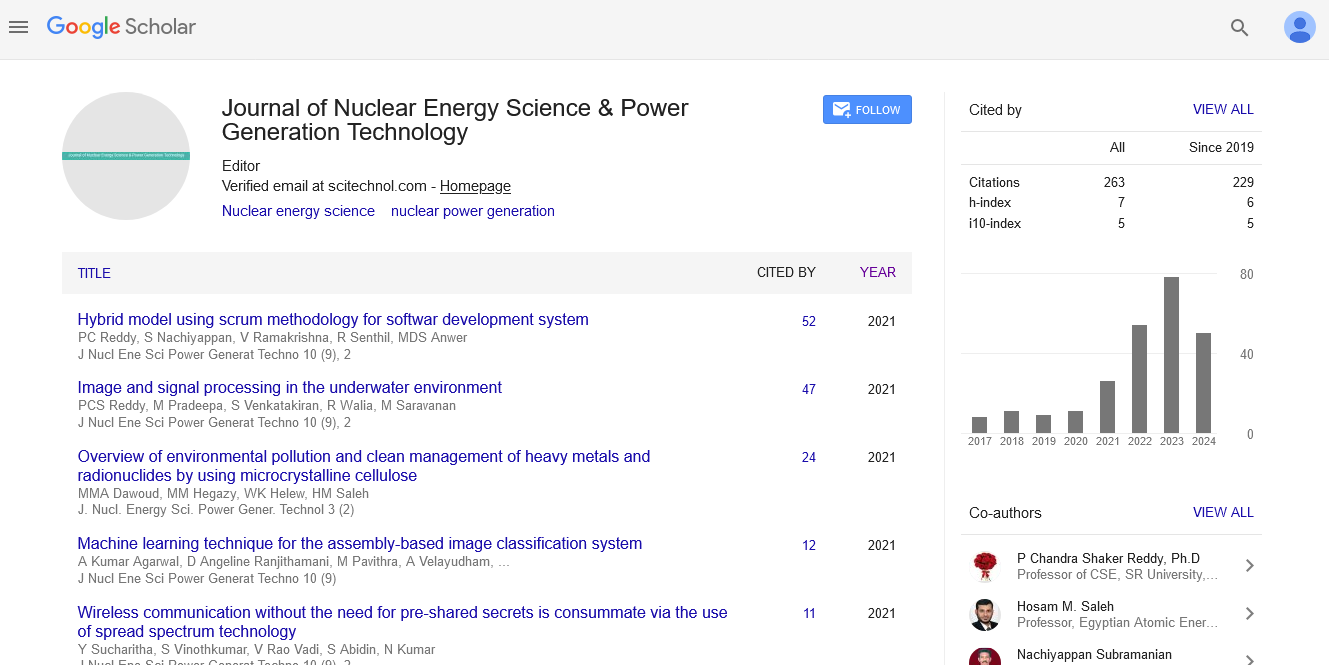
Opinion Article, J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol Vol: 12 Issue: 5
Pebble Bed Reactors: It’s Significance for Low-Carbon Electricity Generation
Mellisa John*
1Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of Texas, Texas, USA
*Corresponding Author: Mellisa John,
Department of Electrical and Computer
Engineering, The University of Texas, Texas, USA
E-mail: meli.sajohn1198@gmail.com
Received date: 30 August, 2023, Manuscript No. JNPGT-23-116484;
Editor assigned date: 01 September, 2023, Pre QC No. JNPGT-23-116484 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 15 September, 2023, QC No. JNPGT-23-116484;
Revised date: 22 September, 2023, Manuscript No. JNPGT-23-116484 (R);
Published date: 29 September, 2023 DOI: 10.4172/2325-9809.1000356.
Citation: John M (2023) Pebble Bed Reactors: It’s Significance for Low-Carbon Electricity Generation. J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol 12:5.
Description
As the world continues to seek sustainable and clean sources of energy, nuclear power remains a significant player in the quest for low-carbon electricity generation. Among the various types of nuclear reactors, Pebble Bed Reactors (PBRs) have emerged as a promising and innovative technology. Pebble Bed Reactors, also known as PBRs, are a type of high-temperature gas-cooled nuclear reactor. They are designed to use spherical fuel elements, often called pebbles, which are typically small graphite spheres containing fissile material. These pebbles are about the size of tennis balls and are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The heart of a Pebble Bed Reactor lies in the fuel spheres.
These spheres contain small pellets of enriched uranium or thorium fuel and are surrounded by layers of graphite. The graphite acts as both a moderator, slowing down neutrons, and a structural support for the fuel. One of the primary advantages of PBRs is their inherent safety features. Due to the pebble configuration and the way the fuel is structured, it's extremely challenging for the reactor to experience a catastrophic meltdown. Even at high temperatures, the fuel remains encapsulated within the pebbles, reducing the risk of nuclear accidents. PBRs are capable of achieving extremely high temperatures, which makes them suitable for various applications, including electricity generation and hydrogen production. The hightemperature output allows for more efficient electricity conversion and thermal applications.
Advantages of pebble bed reactors
As mentioned earlier, the pebble bed design inherently reduces the risk of severe accidents or meltdowns, providing an extra layer of safety, which is important for public acceptance. PBRs' ability to operate at high temperatures makes them highly efficient for electricity generation. The heat produced can be used for various applications, such as power generation and hydrogen production. PBRs generate less long-lived nuclear waste due to their fuel design, which is more efficient in terms of fuel utilization. PBRs can be built as Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), making them easier to construct and manage. This modular design is cost-effective and allows for easier scalability. The high-temperature operation of PBRs can lead to more efficient fuel utilization, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
The production and handling of pebble fuel elements can be complex and costly. PBRs may experience neutron leakage due to the presence of multiple layers of graphite and fuel, which can reduce their efficiency. Over time, the high-temperature environment within the reactor can cause structural materials, such as graphite, to degrade, requiring careful monitoring and maintenance. The initial capital cost of PBRs can be relatively high, and there may be economic challenges to overcome. Pebble Bed Reactors represent a promising technology in the realm of nuclear energy generation. Their inherent safety, high efficiency, and modular design make them an attractive option for clean energy production. However, overcoming the challenges associated with fuel fabrication, neutron leakage, and cost will be key to their successful integration into the future of sustainable energy generation. As research and development continue, PBRs hold the potential to play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and ensuring a more sustainable energy future.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi