Commentary, J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol Vol: 12 Issue: 5
Steam to Power Turbines Process Involves Converting the Thermal Energy
Feni Rei*
1Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan
*Corresponding Author: Feni Rei,
Department of Mechanical Engineering,
National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan
E-mail: fenirei11@gmail.com
Received date: 30 August, 2023, Manuscript No. JNPGT-23-116491;
Editor assigned date: 01 September, 2023, PreQC No. JNPGT-23-116491 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 15 September, 2023, QC No. JNPGT-23-116491;
Revised date: 22 September, 2023, Manuscript No. JNPGT-23-116491(R);
Published date: 29 September, 2023 DOI: 10.4172/2325-9809.1000360.
Citation: Rei F (2023) Steam to Power Turbines Process Involves Converting the Thermal Energy. J Nucl Ene Sci Power Generat Technol 12:5.
Description
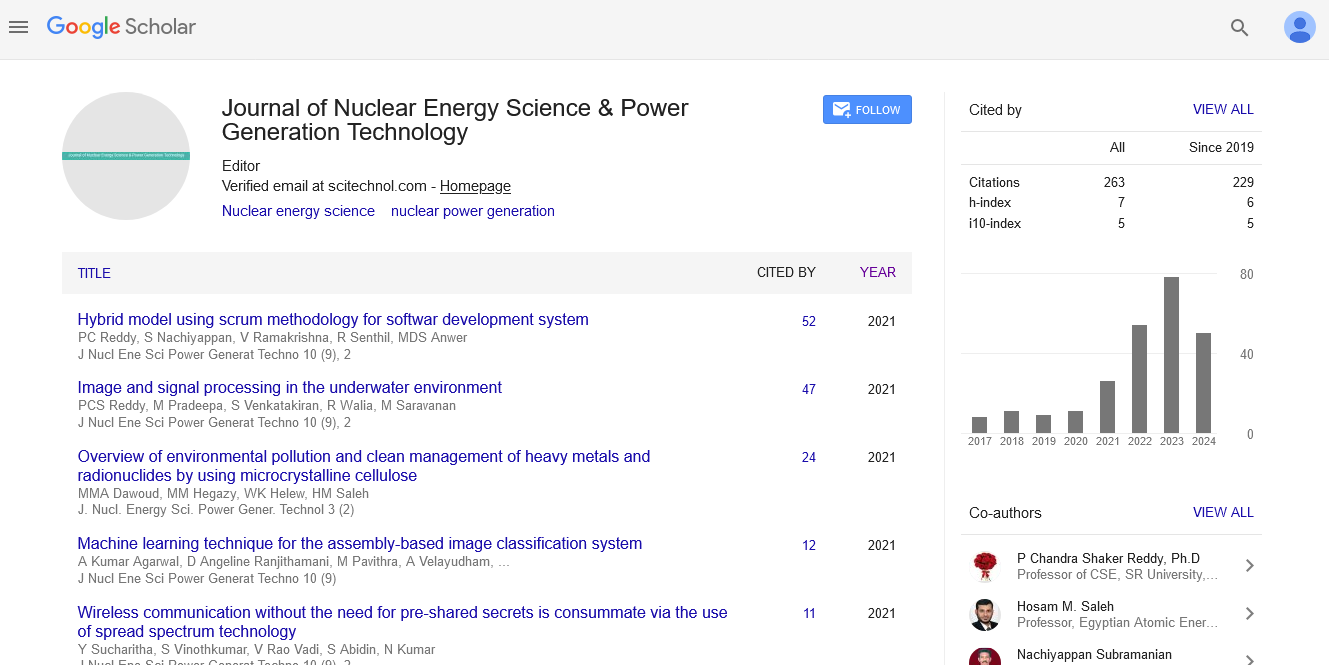
The utilization of steam to run turbines is a cornerstone of modern engineering and power generation. This ingenious process involves converting the thermal energy stored in steam into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electricity or used for various industrial applications. Steam is produced by heating water to its boiling point. In industrial and power plant settings, this is often achieved using large boilers, which can use various fuels, including coal, natural gas, or nuclear energy. The high-pressure steam produced in the boiler is directed to a turbine, where it enters at a controlled rate. As the steam flows through the turbine's blades, it expands, releasing thermal energy and increasing its volume. The expansion of steam results in a significant increase in velocity. The steam's high-speed flow causes the turbine blades to rotate. This rotational motion is the conversion of the thermal energy stored in steam into mechanical energy. The rotating shaft connected to the turbine blades is linked to a generator. As the turbine spins, it drives the generator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
Applications of steam turbines
Steam turbines play a crucial role in electricity generation. They are used in various power plants, including coal-fired, natural gas, nuclear, and geothermal power stations. These turbines can generate massive amounts of electricity efficiently and reliably. Steam turbines are employed in industries such as pulp and paper, petrochemicals, and manufacturing, where they provide mechanical power for driving pumps, compressors, and other equipment. Steam turbines were once widely used in marine propulsion for ships. Although they have been largely replaced by diesel engines and gas turbines, steam turbines are still used in some naval vessels and large ships. Combined Heat And Power (CHP) or cogeneration systems utilize steam turbines to generate both electricity and useful thermal energy for heating or cooling, increasing overall energy efficiency. In geothermal power plants, steam turbines are employed to convert the high-temperature steam extracted from beneath the Earth's surface into electricity.
Advantages of steam turbines
Steam turbines can achieve high levels of efficiency, making them an excellent choice for power generation and industrial applications. Steam turbines are known for their robustness and reliability, making them suitable for continuous and heavy-duty operations. They can use various fuels, making them adaptable to different energy sources and applications. In some configurations, steam turbines can be equipped with emission control technologies to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
While steam turbines are widely used and versatile, Steam turbines are often associated with large-scale power plants, requiring substantial infrastructure and investment. Steam generation can be resource-intensive, especially when non-renewable fuels are used. Steam turbines require regular maintenance and skilled personnel to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The harnessing of steam to power turbines is a testament to human ingenuity and engineering prowess. This process, based on fundamental principles of thermodynamics and fluid dynamics, has powered industries, generated electricity, and driven progress for over a century. And more efficient ways to generate energy, steam turbines remain a vital component of our energy landscape, providing reliable and versatile power generation for a wide range of applications.
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi