Short Communication, Geoinfor Geostat An Overview Vol: 4 Issue: 4
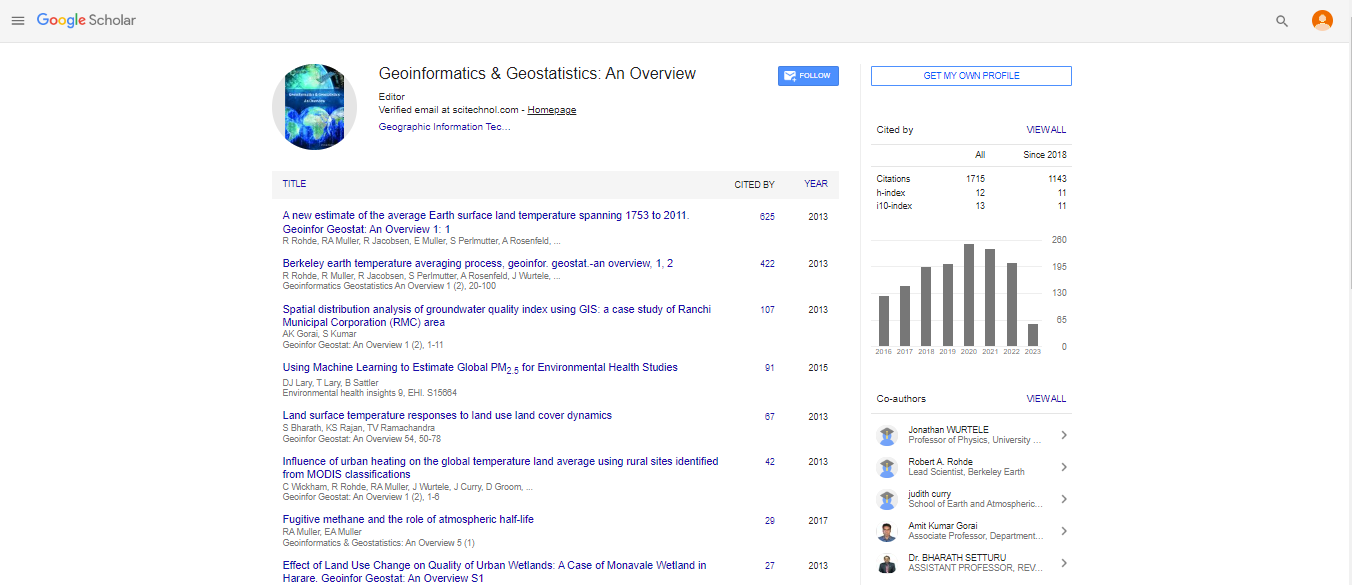
Using Machine Learning to Estimate Global PM2.5 for Environmental Health Studies
| Lary DJ*, Lary T and Sattler B | |
| Hanson Center for Space Sciences, University of Texas at Dallas, Dallas, TX, USA | |
| Corresponding author : David John Lary Hanson Center for Space Sciences, University of Texas at Dallas, Dallas, TX, USA Tel: +1 (972) 489-2059 E-mail: david.lary@utdallas.edu |
|
| Received: March 30, 2016 Accepted: July 09, 2016 Published: July 13, 2016 | |
| Citation: Lary DJ, Lary T, Sattler B (2016) Using Machine Learning to Estimate Global PM2.5 for Environmental Health Studies. Geoinfor Geostat: An Overview 4:4. doi:10.4172/2327-4581.1000149 |
Abstract
There is an increasing awareness of the health impacts of particulate matter and a growing need to quantify the spatial and temporal variations of the global abundance of ground level airborne particulate matter (PM2.5). In March 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a report that in 2012 alone, a staggering 7 million people died as a result of air pollution exposure , one in eight of the total global deaths. A major component of this pollution is airborne particulate matter (e.g. PM2.5 & PM10).
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi