Research Article, J Pharm Sci Emerg Drugs Vol: 13 Issue: 1
Comparative Biowaiver Study of Moxifloxacin in Immediate Release of Oral Solid Dosage Form
Zahid Siraj1,2*, Omair Adil1,2, Bakht Amin3 and Iftikhar Ahmed Tahiri1
1Department of Chemistry, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Sciences and Technology, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi, Pakistan
2Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Sciences, 1245 Lincoln Dr, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL 62901, USA
3Department of Pharmacy, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Sciences and Technology, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi, Pakistan
*Corresponding Author:Zahid Siraj
Department of Chemistry, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Sciences and Technology, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi, Pakistan
E-mail: sirajz@ymail.com
Received date: 11 January, 2024, Manuscript No. JPSED-24-124975;
Editor assigned date: 13 January, 2024, PreQC No. JPSED-24-124975 (PQ);
Reviewed date: 27 January, 2024, QC No. JPSED-24-124975;
Revised date: 11 February, 2025, Manuscript No. JPSED-24-124975 (R);
Published date: 18 February, 2025, DOI: 10.4172/2380-9477.1000204
Citation:Siraj Z, Adil O, Amin B, Tahiri IA (2025) Comparative Biowaiver Study of Moxifloxacin in Immediate Release of Oral Solid Dosage Form. J Pharm Sci Emerg Drugs 13:1.
Abstract
Bio-waiver is based on a Bio-pharmaceutical Classification System (BCS), and it is used to waive in vivo studies of generic test products that are intended for registration from drug regulatory authorities. After certain in vitro testing, the BCS tells whether the test product is “bioequivalent” to the innovator product or not. Bioequivalence is needed to check the risks arising from the presence of different excipients in the formulation and due to manufacturing variables being deemed to be low. Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug with a wide therapeutic index. It shows a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity against both gram-positive and gramnegative pathogens. Here, in vitro biowaiver study of moxifloxacin was conducted based on Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS). Out of four BCS classes, moxifloxacin falls in class I which represents high solubility and high permeability. One innovator and five test brands of moxifloxacin tablets were collected from the local market and their in vitro dissolution study was performed by using pharma test DT 70 apparatus at different time (15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes), in three buffer systems i.e., hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 1.2), acetate buffer (pH 4.5) and phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). Bio-waiver of moxifloxacin tablet is scientifically justified. The dosage form of the innovator product is rapidly dissolving (85% in 15 min) in all three buffers. Interestingly, we found low-cost alternative generic test products that show similar dissolution profiles to the innovator product in these buffers. Therefore, the bio-waiver study of moxifloxacin provides evidence that the generic test products are bioequivalent with innovator products which leads to provision of cost effective and alternative drug product.
Keywords: Biopharmaceutical classification system; Innovator product; Generic product
Abbreviation
BCS: Bio-pharmaceutics Classification System; U.S: United States; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; EMA: European Medicines Agency; ICH: International Council for Harmonization Guidance; WHO: World Health Organization; IR: Immediate Release; API: Active Pharmaceuticals Ingredients; CoA: Certificate of Analysis; DRAP: Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan; UV: Ultra-Violet
Introduction
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic [1]. It is a broad range spectrum antibacterial medicine. Its antibacterial activity is effective against both types of gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens. Its clinical studies confirmed that it is a well-tolerated drug and has high efficacy against pneumonia acute bacterial rhino sinusitis and chronic bronchitis [2-6].
Bio-waiver is based on a Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS). A more precise term “BCS based bio-waiver” is used to waive in vivo studies of test products that are intended for registration. There are four BCS classes. Bio-waiver can be performed based on U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) Guidance, and the World Health Organization (WHO) for the registration of new or re-formulated Immediate Release (IR) solid oral dosage forms. Those pharmaceutical drugs that belong to BCS class I has high solubility and high permeability and accredited as a successful bio-waiver candidate. For the bio-waiver studies the bioequivalence testing is not prerequisite. In vitro dissolution profile is used to evaluate whether the pharmaceutical test product is equivalent to the innovator. FDA and ICH recommended the immediate release dosage form containing Active Pharmaceuticals Ingredients (API) belonging to BCS class I and III. Different regulatory authorities, including 2006 WHO guidelines proposed that, to pass the BCS class I bio-waiver, the multisource product must dissolve 85% or more within 30 minutes of its release in all three buffers i.e. phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), acetate buffer (pH 4.5) and HCl buffer (pH 1.2) [7].
Following the WHO guidelines, in vitro bio-waiver study of moxifloxacin is conducted with the innovator drug product and five different inexpensive alternative generic products [8]. Since, the reference product, moxifloxacin 400 mg tablets falls in BCS class I which represents high solubility and high permeability is manufactured by a multinational company, while the five different test products were produced by local pharma companies in Pakistan [9,10]. We performed their in vitro dissolution study by using pharma test DT 70 apparatus at different time intervals (15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes) in three different buffer systems i.e., hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 1.2), acetate buffer (pH 4.5) and phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). We took dissolved tablet solution and calculated the percent dissolution from the UV-visible absorbance at wavelength 293 nm. After that we use standard equation models to obtain the similarity factor and difference factor. The similarity factor (f2) of each generic product determines whether the test products are bioequivalent to the reference product or not. The whole process is present in Figure 1. We further perform cost analysis to find if the test product can be an inexpensive alternative to the reference product to present study where local and low-cost alternative drug can be acquired for under privilege community. In this study we found that a simple in vitro bio-waiver study, as per the WHO guidelines, is a valuable tool to determine the quality of low-cost alternatives of drugs compare to the more costly innovator drug.
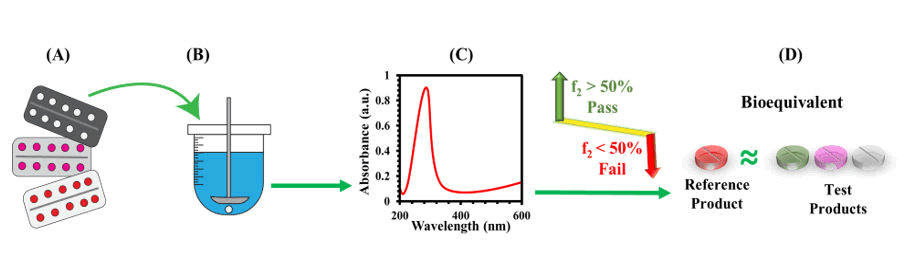
Figure 1: Schematic representation of bio waiver study of five different generic test drugs in comparison with reference product. A) Tablets of one reference and five different generic test brands were collected from local market. B) Dissolution studies performed in three different buffer media at different times. C) UV-vis studies after dissolution D) Similarity factor calculation of generic test products against reference product to determine bioequivalence.
Materials and Methods
Moxifloxacin HCl was received from INDUS pharma Karachi, Pakistan and used as a working standard, Batch No. EL-03/L011/M/ 14138, Manufacturer, Enaltec Labs Chemistry, from India. The reading of the potency of Moxifloxacin HCl on anhydrous basis and their moisture content were taken from the Certificate of Analysis (CoA) provided by the vendor i.e., 99.81% and 3.59% respectively. Six different alternative brands of moxifloxacin 400 mg tablets were purchased from the local pharmacy of Karachi Pakistan. All these brands were registered by the Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan (DRAP). All tests were performed within the product expiry dates. The innovator brand was labeled as “M” while the generic test products are labelled as “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5” as listed in Table 1.
| Product ID | Products | Batch number | Manufacture date | Expiry | MRP (PKR) |
| M | Innovator/Reference | BXGPE71 | 02/2014 | 01/2018 | 790 |
| P1 | Generic test product 1 | 125F31 | 11/2014 | 11/2016 | 375 |
| P2 | Generic test product 2 | 6 | 07/2014 | 07/2016 | 475 |
| P3 | Generic test product 3 | 6299 | 03/2014 | 03/2016 | 394 |
| P4 | Generic test product 4 | 112689 | 08/2014 | 08/2016 | 175 |
| P5 | Generic test product 5 | 2V | 07/2014 | 07/2016 | 250 |
Table 1: List of one reference and five generic test brands of moxifloxacin 400 mg tablets, with their ID used in this paper. The manufacturing and expiry dates mentioned month and year. The Manufacturing Retail Price (MRP) is showing price of five tablets in Pakistani currency (PKR), according to the price in 2014.
The instruments used in the bio-waiver studies are Karl Fischer potentiometer from Mettler Toledo, Switzerland, analytical five digits balance from Sartorius CP225D, Germany. Dissolution apparatus, pharma test, DT 70, from Germany, pH Meter Orion, 312, USA, UVvis spectrophotometer, Shimadzu, UV-1800, Japan. All analytical grade reagents, disodium tartrate dihydrate (≥ 99%.), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (≥ 99%.), phosphoric acid (≥ 85%.), potassium chloride (≥ 99%.), hydrochloric acid (≥ 37%.), sodium acetate trihydrate (≥ 99%.), acetic acid (≥ 99%.) and sodium hydroxide (≥ 97%.), were purchased from Merck KGaA, Germany.
Percentdissolutionandbio-waiverstudyoftestproducts
The dissolution study was performed by using pharma test DT 70 apparatus. It contained seven units (vessels), six units used for testing product while the seventh was used for blank. Dissolution was performed on 12 tablets of each product [11]. So, bio-waiver in vitro dissolution study was performed in three media i.e., 0.1 N HCl buffer (pH 1.2), acetate buffer (pH 4.5) and phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). Temperature was kept constant throughout the study i.e., 37°C ± 0.5°C. One mL samples collected at 15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes, while one mL media from blank unit (vessel) replaced. Rotation was kept constant at 75 cycles per min throughout the study. while the in vitro dissolution study was carried out in two phases i.e., first stage and second stage because the maximum capacity of the dissolution apparatus Pharma test DT 70 was eight vessels in which six vessels were used for products while one used for blank media (0.1 N HCl). The same methodology is used for the other two buffers. The concentration of the API in generic and reference products was determined by using spectrophotometer UV-vis 1800 (Shimadzu) at wavelength 293 nm.
A dissolution test is performed based on the following equation.
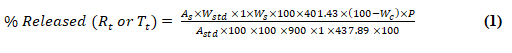
Where,
AS=Absorbance of sample,
WStd=Weight of Standard,
WS=Weight of Sample, molecular mass of Moxifloxacin as base=401.43 g,
Molecular mass of Moxifloxacin as salt=437.89 g,
Wc=Water content,
P=Potency of Moxifloxacin as on anhydrous basis.
AStd=Absorbance of standard (moxifloxacin HCl). Absorbance of standard in 0.1N HCl=0.514 Absorbance of standard in acetate buffer (pH 4.5)=0.504 Absorbance of standard in phosphate buffer (pH 6.8)=0.386. These were the absorbance of standard (Moxifloxacin HCl) used in the calculation for % dissolved in each buffer in Equation 1.
The in vitro bio-waiver is considered based on similarity factor f2 (calculated from Equation 2) and difference factor f1 (calculated from Equation 3) between test product and reference product. Bio-waiver is considered very rapid if the similarity factor f2 is greater than 85% in 15minutes.

Results
In vitro dissolution comparative study of one innovator and five generic test products were performed first in 0.1N HCl buffer pH 1.2 at different times. The results were obtained as % dissolved of the moxifloxacin in 0.1N HCl with pH 1.2 as shown in Table 2. It was observed that all the test products show the % dissolved of moxifloxacin greater than 90% after 15 minutes. The increasing trend was observed after 30 min, 45 min and finally after 60 minutes it was greater than 95% dissolved of the moxifloxacin. So, it scientifically justified that moxifloxacin falls in BCS class I and has high solubility and high permeability. The % dissolution trend of the innovator brand “M” of moxifloxacin versus the generic test product “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5” in 0.1N HCl is shown in Figure 2a. The results of all the test products of % dissolved of the moxifloxacin in 0.1N HCl with pH 1.2 were used in the calculation of similarity factor (f2) and the difference factor or dissimilarity factor (f1).
| n | M (Rt) % | P1 (Tt) % | P2 (Tt) % | P3 (Tt) % | P4 (Tt) % | P5 (Tt) % |
| 15 | 101.75 | 101.18 | 93.67 | 97.01 | 98.34 | 96.12 |
| 30 | 100.63 | 100.7 | 95.45 | 96.68 | 100.11 | 95.74 |
| 45 | 100.64 | 99.48 | 94.14 | 96.83 | 99.78 | 95.4 |
| 30 | 99.81 | 98.16 | 93.62 | 95.95 | 98.58 | 94.1 |
Table 2: Average % dissolved (Moxifloxacin) between innovator product “M” and generic test products tablet (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in pH 1.2 HCl at 293 nm.
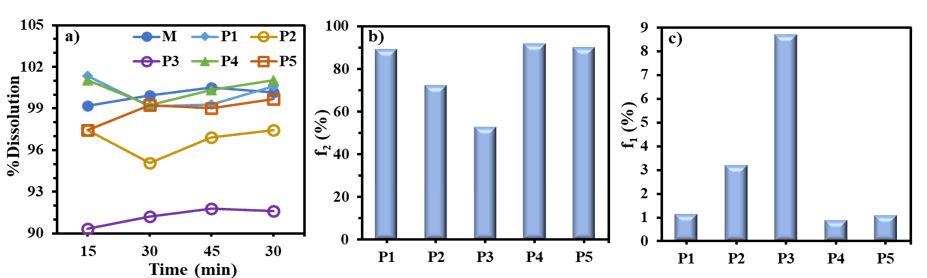
In vitro comparative study of moxifloxacin in BCS class I all the test products show the similarity factor greater than 50% and difference factor less than 20% with the innovator product. In among all generic test products “P1” shows maximum similarity factor i.e., 91.95% and low difference factor 0.86% with the innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin tablet 400 mg) while “P2” shows the least similarity factor i.e., 58.87% and greater difference factor 6.44%. So, all generic products that were manufactured locally with different brand name fulfill the requirement of the bio-waiver by showing the similarity factor greater than 50% and difference factor less than 20% with innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin tablet 400 mg) in 0.1 N HCl with pH 1.2 as shown in Figure 2b and Figure 2c respectively. Therefore, all test products are bioequivalent to the innovator product in 0.1 N HCl with pH 1.2.
Figure 2: A) Average % dissolution (Moxifloxacin) comparison between reference drug product “M” and the test drug products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) at wavelength 293 nm in HCl buffer at pH 1.2. B) Similarity factor between reference drug product “M” and test products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in pH 1.2 HCl buffer at 293 nm. C) Difference factor between reference drug product “M” and test products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in 1.2 pH HCl buffer at 293 nm.
In vitro dissolution comparative study of moxifloxacin was carried out in acetate buffer with pH 4.5. By this study the results were obtained as % dissolved of the moxifloxacin in acetate buffer with pH 4.5. It was observed that except “P3” all the test products show the % dissolved of moxifloxacin greater than 95% after 15 minutes in acetate buffer with pH 4.5. The increased in trend was observed after 30 min, 45 min and finally after 60 minutes it was greater than 95% dissolved of the moxifloxacin while P3 shows % dissolved of moxifloxacin greater than 90% after 15 minutes and slight increase in trend was observed after 30 min, 45 min and finally after 60 min it was below 95%. So, the study carried in acetate buffer with pH 4.5 provided evidence that moxifloxacin falls in BCS class I and has high solubility and high permeability. The results were obtained as % dissolved of moxifloxacin as shown in Table 3. The % dissolution trend of the innovator brand “M” of moxifloxacin versus the generic test product “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5” in acetate buffer with pH 4.5 is shown in Figure 3a. These results were used in the calculation of similarity factor (f2) and the difference factor (f1) of moxifloxacin in acetate buffer with pH 4.5.
| n | M (Rt) % | P1 (Tt) % | P2 (Tt) % | P3 (Tt) % | P4 (Tt) % | P5 (Tt) % |
| 15 | 99.2 | 101.35 | 97.46 | 90.35 | 101.02 | 97.44 |
| 30 | 99.96 | 99.17 | 95.06 | 91.22 | 99.25 | 99.25 |
| 45 | 100.53 | 99.3 | 96.93 | 91.81 | 100.33 | 99.04 |
| 30 | 100.14 | 100.6 | 97.46 | 91.6 | 101.02 | 99.66 |
Table 3: Average % dissolved (Moxifloxacin) between innovator product “M” and generic test products tablet (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in pH 4.5 acetate buffer at 293 nm.
The biowaiver in vitro study of innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) and the generic test products (locally manufactured) in acetate buffer pH 4.5 show the % dissolved of moxifloxacin greater than 90% after 15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes as shown in Table 3. These results were used in the calculation of similarity and difference factor of moxifloxacin in BCS class I. It was observed that all the test products show the similarity factor (f2) greater than 50% and difference factor (f1) less than 20% with the innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) in acetate buffer pH 4.5. In among all generic test product “P4” shows maximum similarity factor i.e., 91.63% and low difference factor 0.91 % with the innovator product while “P3” shows the least similarity factor i.e., 52.86% and greater difference factor 8.71% in acetate buffer pH 4.5 as shown in Figure 3b and Figure 3c. So, all generic test products that were manufactured locally with different brand names fulfill the requirement of the biowaiver in acetate buffer pH 4.5.
Figure 3: A) % Dissolution (Moxifloxacin) comparison between reference drug product “M” and the generic test drug products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) at wavelength 293 nm in acetate buffer at 4.5 pH. B) Similarity factor between reference drug product “M” and test products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in pH 4.5 acetate buffers at 293 nm. C) Difference factor between reference drug product “M” and generic test drug products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in 4.5 pH acetate buffers at 293 nm.
For bio-waiver in vitro dissolution comparative study of moxifloxacin of one innovator and five generic test products was carried out in phosphate buffer with pH 6.8 and the results were obtained as % dissolved of the moxifloxacin as shown in Table 4. All the parameters were kept constant during the whole in vitro dissolution comparative study of all test products in phosphate buffer with pH 6.8 except the media (Phosphate buffer with pH 6.8). It was observed that except “P3” other all test products show the % dissolved of moxifloxacin greater than 95% after 15 minutes in Phosphate buffer with pH 6.8. The increase in trend was observed after 30 min, 45 min. After 60 minutes it was greater than 95% dissolved of the moxifloxacin while “P3” shows % dissolved of moxifloxacin greater than 90% after 15 minutes and slight increase in trend was observed after 30 min, 45 min. After 60 min it was below 95%. So, it scientifically justified that moxifloxacin falls in BCS class I and has high solubility and high permeability in phosphate buffer with pH 6.8. The % dissolution trend of the innovator brand “M” of moxifloxacin versus the test product “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5” in phosphate buffer with pH 6.8 is shown in Figure 4a.
| n | M (Rt)% | P1 (Tt)% | P2 (Tt)% | P3 (Tt)% | P4 (Tt)% | P5 (Tt) % |
| 15 | 97.28 | 98.67 | 91.69 | 97.43 | 93.96 | 97.71 |
| 30 | 97.18 | 98.46 | 92.63 | 97.88 | 95.03 | 98.59 |
| 45 | 97.56 | 99.04 | 93.32 | 98.42 | 95.42 | 99.26 |
| 30 | 98.34 | 99.39 | 93.49 | 98.72 | 96.47 | 99.62 |
Table 4: Average % dissolution between innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) and generic test products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) tablet in pH 6.8 phosphate buffer at 293 nm.
Further the data obtained as % dissolved of moxifloxacin from Table 4 were used in the calculation of similarity and difference factor of moxifloxacin in BCS class I. it was observed that all the test products show the similarity factor (f2) greater than 50% and difference factor (f1) less than 20% with the innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) in phosphate buffer pH 6.8. In among all generic test product “P2” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) shows maximum similarity factor i.e., 96.73% and low difference factor 0.54% with the innovator product while “P3” shows the least similarity factor i.e., 65.31% and greater difference factor 4.93% in phosphate buffer pH 6.8 as shown in Figure 4b and Figure 4c respectively. So, all generic test products that were manufactured locally with different brand names fulfill the requirement of the bio-waiver in phosphate buffer pH 6.8.
Figure 4: A) % Dissolution (Moxifloxacin) comparison between reference drug product “M” and the generic test drug products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) at wavelength 293 nm in phosphate buffer at 6.8 pH. B) Similarity factor between reference drug product “M” and test products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in 6.8 pH phosphate buffers at 293 nm. C) Difference factor between reference drug product “M” and generic test drug products (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) in pH 6.8 phosphate buffers at 293 nm.
Discussion
Based on BCS, the in vitro bio-waiver study of moxifloxacin, an antibiotic, was conducted on an innovator product ("M") and five test products "P1, P2, P3, P4, P5" in three buffers media i.e., hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 1.2), acetate buffer (pH 4.5) and phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) [12,13]. The percent dissolution data in 0.1N HCl buffer showed that all the test products exhibit more than 90% dissolution rate after 15 minutes. The increased trend was observed for another 60 minutes, until it eventually exceeded 95%. The percent dissolution in 0.1N HCl is graphically depicted in Figure 2a, which also shows that all test products and innovator products have similar percent dissolution.
Further, the obtained percentage dissolution data of the innovator product “M” and test products "P1, P2, P3, P4, P5" in 0.1N HCl used for the quantification of the similarity factor (f2) and the difference factor (f1). Among the test products, "P1" indicated the highest similarity factor (91.95%) and the lowest difference factor (0.86%) with the innovator product "M." Conversely, “P2" exhibited the least similarity factor (58.87%) and a higher difference factor (6.44%). The results suggest that all locally manufactured test products "P1, P2, P3, P4, P5" despite having different brand names, meet the criteria for biowaiver, indicating bioequivalence with the innovator product “M” in 0.1N HCl buffer with pH 1.2. Therefore, all the test products are bioequivalent to the innovator product in 0.1N HCl with pH 1.2 [14].
The study further conducted on the percent dissolution of moxifloxacin between innovator product “M” and test products "P1, P2, P3, P4, P5" in acetate buffer at pH 4.5. The percent dissolution of moxifloxacin from both the innovator and test products exceeded 90% after 15, 30, 45, and 60 minutes, satisfying the dissolution profiles criteria of the immediate release product. Further, the similarity factor (f2) and difference factor (f1) were calculated to assess the similarity between the dissolution profiles of the test and innovator products. Among the test products, “P4” demonstrated the highest similarity factor (91.63%) and the lowest difference factor (0.91%) with the innovator product “M”. In contrast, “P3” showed the least similarity factor (52.86%) and a higher difference factor (8.71%). The results suggest that all locally manufactured generic products, despite having different brand names, meet the criteria for bio-waiver in acetate buffer pH 4.5 [15]. The high similarity factors indicate that the dissolution profiles of the test products “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5" closely resemble that of the innovator product “M”, supporting the bioequivalence of these formulations.
The bio-waiver in vitro dissolution comparative study of moxifloxacin was also conducted in phosphate buffer with pH 6.8 that involves one innovator “M” and five test products "P1, P2, P3, P4, P5". Except for “P3”, all test products demonstrated moxifloxacin dissolution greater than 95% after 15 minutes in phosphate buffer with pH 6.8. The dissolution trend continued to increase after 30 minutes and 45 minutes, with all products surpassing 95% dissolution after 60 minutes. “P3” exhibited a slightly different dissolution profile, with moxifloxacin dissolution greater than 90% after 15 minutes. The increase in trend was observed after 30 and 45 minutes, but after 60 minutes, the dissolution was below 95%. Moreover, the similarity factor (f2) and the difference factor (f1) of the innovator and test products were calculated in phosphate buffer at pH 6.8. Among the generic products, “P2” exhibited the highest similarity factor (96.73%) with the innovator product. This indicates a very close similarity in the dissolution profiles of “P2” and the innovator product in the phosphate buffer at pH 6.8. “P3”, on the other hand, showed the least similarity factor (65.31%) and a higher difference factor (4.93%). This suggests some variability in the dissolution profile of “P3” compared to the innovator product in phosphate buffer pH 6.8. Despite the variability observed in “P3”, the fact that it still meets the regulatory criteria for similarity and difference factors supports the overall conclusion that all locally manufactured generic products fulfill the bio-waiver requirements in phosphate buffer pH 6.8.
During the complete dissolution profile studies in all three buffers media the variation in trend in % dissolution of the test products “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5” versus the innovator product “M” are observed which is mainly associated with the excipients in the dosage form that impact on the % release of the moxifloxacin in the buffer media [16,17]. In addition the particle size and polymorphic form as well as potential interactions of API with excipients should be taken into account [18-20]. The different source of the API affects the bio-waiver by affecting solubility, dissolution and permeability. However, it is concluded from the dissolution profile study of moxifloxacin that all the generic products that were manufactured locally were bioequivalent to the innovator product in all three buffer media with different pH 1.2, 4.5, 6.8. So, it provided provision for alternative drug product and cost effectiveness and builds confidence on the locally manufactured products.
Conclusion
In vitro bio-waiver study of moxifloxacin was conducted based on Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS). Moxifloxacin falls in BCS class I and has high solubility and high permeability. Moxifloxacin tablets of innovator and five different brands were collected from the local market and performed their in vitro dissolution study by using pharma test DT 70 apparatus in three buffers having pH 1.2, 4.5, and 6.8.
A biowaiver for moxifloxacin solid oral dosage form is scientifically justified and indicates that the dosage form is rapidly dissolving >85% in 15 min in pH 1.2, 4.5, and 6.8. The all-generic test products showed greater than 50 percent similarities to the reference product and difference factor less than 20 percent. While the variation in trend in % dissolution of the generic test products “P1, P2, P3, P4, P5” versus the innovator product “M” in all three buffers media was observed which is attributed with the excipient which plays an important role in the % release of the moxifloxacin. The test product “P4” is the most low-cost product among all but showed more than 80 percent similarities to the innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) in all three buffers media that builds confidence in locally manufactured product and lead provision of low cost and alternative drug product. Therefore, biowaiver gives evidence that the test products are bioequivalent to the innovator product “M” (moxifloxacin 400 mg tablet) that gives provision of cost effective and alternative product.
References
- Charoo NA, Abdallah DB, Parveen T, Abrahamsson B, Cristofoletti R, et al. (2020) Biowaiver monograph for immediate-release solid oral dosage forms: Moxifloxacin hydrochloride. J Pharm Sci 109: 2654-2675.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Welte T, Petermann W, Schurmann D, Thomas Bauer T, Reimnitz P, et al. (2005) Treatment with sequential intravenous or oral moxifloxacin was associated with faster clinical improvement than was standard therapy for hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia who received initial parenteral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 41: 1697-1705.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finch R, Schurmann D, Collins O, Kubin R, McGivern J, et al. (2002) Randomized controlled trial of sequential Intravenous (iv) and oral moxifloxacin compared with sequential iv and oral co-amoxiclav with or without clarithromycin in patients with community-acquired pneumonia requiring initial parenteral treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46: 1746-1754.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anzueto A, Niederman MS, Pearle J, Restrepo MI, Heyder A, et al. (2006) Community-Acquired Pneumonia Recovery in the Elderly (CAPRIE): Efficacy and safety of moxifloxacin therapy versus that of levofloxacin therapy. Clin Infect Dis 42: 73-81.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikov AY, Edzhe MA, Miroshnichenko NA, Hon EM, Korostelev SA (2015) 15-year experience of moxifloxacin in the treatment of patients with bacterial rhinosinusitis. Vestn Otorinolaringol 80: 75-79.
[Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt O, Welte T (2009) 10 years’ experience with the pneumococcal quinolone moxifloxacin. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 7: 645-668.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barends D, Dressman J, Hubbard J, Junginger H, Patnaik R, et al. (2005) Multisource (generic) pharmaceutical products: guidelines on registration requirements to establish interchangeability draft revision. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Miranda C, Perez-Rodriguez Z, Hernandez-Armengol R, Quinones-Garcia Y, Betancourt-Puron T, et al. (2018) Biowaiver or bioequivalence: Ambiguity in sildenafil citrate BCS classification. AAPS PharmSciTech 19: 1693-1698.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogt M, Derendorf H, Kramer J, Junginger HE, Midha KK, et al. (2007) Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oraldosage forms: Prednisolone. J Pharm Sci 96: 27-37.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalid F, Hassan SM, Mushtaque M, Noor R, Ghayas S, et al. (2020) Comparative analysis of biopharmaceutic classification system (BCS) based biowaiver protocols to validate equivalence of a multisource product. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 14: 212-220.
- Lazo RE, Teleginski LK, Maciel AB, Silva MA, Mendes C, et al. (2022) Comparator product issues for biowaiver implementation: The case of Fluconazole. Braz J Pharm Sci 58: e19710.
- Davit BM, Kanfer I, Tsang YC, Cardot JM (2016) BCS biowaivers: Similarities and differences among EMA, FDA, and WHO requirements. The AAPS J 18: 612-618.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benet LZ, Larregieu CA (2010) The FDA should eliminate the ambiguities in the current BCS biowaiver guidance and make public the drugs for which BCS biowaivers have been granted. Clin Pharmacol Ther 88: 405-407.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flanagan T (2019) Potential for pharmaceutical excipients to impact absorption: A mechanistic review for BCS Class 1 and 3 drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 141: 130-138.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Metry M, Polli JE (2022) Evaluation of excipient risk in BCS class I and III biowaivers. The AAPS J 24: 20.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao C, Jain A, Hailemariam L, Suresh P, Akkisetty P, et al. (2006) Toward intelligent decision support for pharmaceutical product development. J Pharm Innov 1: 23-35.
- Ku MS (2008) Use of the biopharmaceutical classification system in early drug development. AAPS J 10: 208-212.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Byrn S, Pfeiffer R, Ganey M, Hoiberg C, Poochikian G (1995) Pharmaceutical solids: A strategic approach to regulatory considerations. Pharml Res 12: 945-954.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang LF, Tong WQ (2004) Impact of solid state properties on developability assessment of drug candidates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56: 321-334.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babu GN, Kumar A, Kalita J, Misra UK (2008) Pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of tuberculous meningitis patients. Neurosci Lett 436: 48-51.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi